Test Autoscaling of Cluster and Application
We added same labels (intent: apps and eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType: SPOT) and taint (spotInstance: “true:PreferNoSchedule”) to EKS managed node groups and Self managed node groups, therefore the same example service can be scaled on both types of node groups.
If you are starting with self managed Spot workers chapter directly and planning to run only self managed node groups with Spot Instances, then complete below chapters and proceed to cleanup chapter directly. Deploy an example Microservice Autoscale Cluster and Application
If you are have already completed EKS managed Spot workers chapters and still want to explore self managed node groups with Spot Instances, then continue with this chapter.
At this point we have 5 node groups in our cluster:
- One EKS managed node group with On-Demand capacity (mng-od-m5large)
- Two EKS managed node groups with Spot capacity (mng-spot-4vcpu-16gb and mng-spot-8vcpu-32gb)
- Two self managed node groups with Spot Instances (ng-spot-4vcpu-16gb and )
Stress test the application
Let’s do a repeat of earlier Stress test with double the number of requests. We will test to see if stressing the same application can trigger autoscaling of both EKS managed node groups with Spot capacity and self managed node groups with Spot Instances.
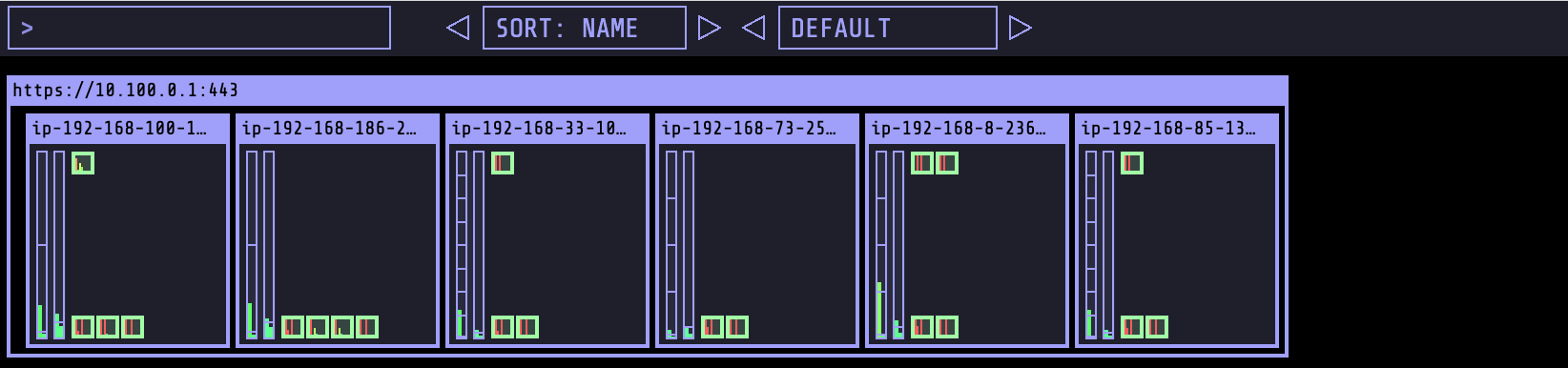
Before starting the stress test, predict what would be the expected outcome. Use kube-ops-view to verify that the changes you were expecting to happen, do in fact happen over time.
Execute the following command on Cloud9 terminal
kubectl get svc kube-ops-view | tail -n 1 | awk '{ print "Kube-ops-view URL = http://"$4 }'
Run the stress test ! This time around we will run 4000 requests (as we have twice the capacity) each expected to take ~1.3sec or so.
time ~/environment/submit_mc_pi_k8s_requests/submit_mc_pi_k8s_requests.py -p 100 -r 40 -i 30000000 -u "http://${URL}"
To display the progress of the rule was setup in Horizontal Pod Autoscaler we can run:
kubectl get hpa -w
This should show the current progress and target pods, and refresh a new line every few seconds.
:~/environment $ kubectl get hpa -w
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 0%/50% 3 100 0 11s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 50%/50% 3 100 6 15s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 100%/50% 3 100 3 75s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 100%/50% 3 100 6 90s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 60%/50% 3 100 6 2m16s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 100%/50% 3 100 6 3m16s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 100%/50% 3 100 12 3m31s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 74%/50% 3 100 21 7m17s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 80%/50% 3 100 21 8m17s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 14%/50% 3 100 21 9m17s
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 14%/50% 3 100 21 10m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 14%/50% 3 100 21 11m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 14%/50% 3 100 21 14m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 50%/50% 3 100 6 14m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 33%/50% 3 100 6 18m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 30%/50% 3 100 6 21m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 0%/50% 3 100 6 22m
monte-carlo-pi-service Deployment/monte-carlo-pi-service 0%/50% 3 100 6 23m
To display the node or pod you can use
kubectl top nodes
or
kubectl top pods
Cluster Autoscaler will use default random expander to scale both types of node groups providing they have matching labels and taints.
After some time, you should be able to confirm that running kubectl get nodes return both self managed and EKS managed Spot nodes:
kubectl get nodes --label-columns=alpha.eksctl.io/nodegroup-name,eks.amazonaws.com/capacityType,type
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODEGROUP-NAME CAPACITYTYPE TYPE
ip-192-168-111-213.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 22h v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e mng-od-m5large ON_DEMAND
ip-192-168-140-47.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 22h v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e mng-od-m5large ON_DEMAND
ip-192-168-189-229.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 3h2m v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e mng-spot-4vcpu-16gb SPOT
ip-192-168-34-125.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 3m3s v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e ng-spot-4vcpu-16gb SPOT self-managed-spot
ip-192-168-6-44.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 3m8s v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e ng-spot-4vcpu-16gb SPOT self-managed-spot
ip-192-168-64-221.ap-southeast-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m v1.21.4-eks-033ce7e ng-spot-4vcpu-16gb SPOT self-managed-spot
You should also be able to visualize the scaling action using kube-ops-view. Kube-ops-view provides an option to highlight pods meeting a regular expression. All pods in green are monte-carlo-pi-service pods.