AWS Batch
Overview
AWS Batch enables developers, scientists, and engineers to easily and efficiently run hundreds of thousands of batch computing jobs on AWS. AWS Batch dynamically provisions the optimal quantity and type of compute resources (e.g., CPU or memory optimized compute resources) based on the volume and specific resource requirements of the batch jobs submitted. AWS Batch plans, schedules, and executes your batch computing workloads across the full range of AWS compute services and features, such as AWS Fargate, Amazon EC2 and Spot Instances. There is no additional charge for AWS Batch. You only pay for the AWS resources you create to store and run your batch jobs.
Thanks to AWS Batch computing, you can execute a series of “jobs” on one or more computers without manual intervention. Input parameters are pre-defined through scripts, command-line arguments, control files, or the AWS Batch job control language. You can make a batch job to depend on the completion of preceding jobs, or on the availability of certain inputs, making the sequencing and scheduling of multiple jobs easy.
AWS Batch features
- Dynamic compute resource provisioning and scaling: you only need to set up a few concepts in AWS Batch (a Compute environment, job queue, and job definition), and you have a complete queue, scheduler, and compute architecture without managing a single piece of compute infrastructure.
- AWS Batch with EC2 Spot instances: AWS Batch workloads are usually a perfect fit for Spot Instances. If a workload is interrupted, AWS Batch will automatically retry the task and spin-up another Spot Instance using AWS EC2 Spot Best practices.
- AWS Batch with Fargate: AWS Batch integrates with AWS Fargate. With AWS Fargate you can run batch workloads in a completely serverless environment.
- Integration with EC2 Launch Templates: AWS Batch does supports EC2 Launch Templates, allowing you to build customized compute resources, and enabling AWS Batch to scale instances with those requirements.
- Priority-based job scheduling: AWS Batch enables you to set up multiple queues with different priority levels. Batch jobs are queued until compute resources are available to execute the job. The AWS Batch scheduler evaluates when, where, and how to run jobs that have been submitted to a queue based on the resource requirements of each job.
If you want to learn in detail all its capabilities, visit this web page.
Understanding Batch components
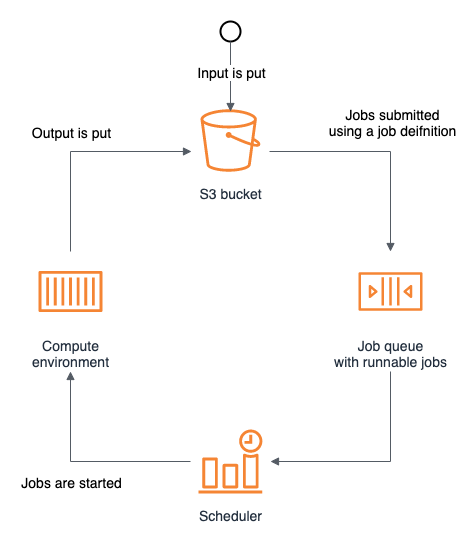
In this section we will go through each individual AWS Batch architecture component, starting with the typical AWS Batch job architecture. In the diagram below you can see how:
- The user starts triggering an event by uploading a S3 object.
- You can automate and trigger the submission of one or more jobs using AWS Lambda or manage AWS Batch with Step functions. The job gets submitted to a Job queue using a Job Definition.
- AWS Batch will schedule the jobs submitted using Compute Environments. It will procure new resources when needed and allocate the job accordingly.
- The Compute Environment resources (EC2 Instances or Fargate) will run the job and store the output in S3 (as in this workshop).
Compute environment
An AWS Batch Compute Environment is a collection of compute resources on which jobs are executed. AWS Batch supports two types of Compute Environments; Managed Compute Environments which are provisioned and managed by AWS and Unmanaged Compute Environments which are managed by customers.
With Managed Compute environments, you can use the following instance configurations:
- Fargate: Allows AWS Batch to run containers without having to manage servers or clusters of Amazon EC2 instances.
- Fargate Spot: Fargate Spot allows you to run interruption tolerant AWS Batch jobs at up to a 70% discount off the Fargate price.
- On-demand: EC2 instances that are billed per second.
- Spot: save money by using EC2 spare capacity.
To learn more about Compute environments, visit AWS Batch Compute environment.
Job queue
Jobs are submitted to a job queue where they reside until they can be scheduled to run in a compute environment. You can configure several job queues. Job queues have a priority that’s used by the scheduler to determine which jobs in which queue should be evaluated for execution first.
To learn more about Job queues, visit AWS Batch Job queues.
Job definition
A Job Definition describes the job to be executed, parameters, environmental variables, compute requirements, and other information that is used to optimize the execution of a job. Job Definitions are defined in advance of submitting a job and can be shared with others.
To learn more about Job definitions, visit AWS Batch Job definitions.
When you should use AWS Batch
AWS Batch can be used in several scenarios where you can split a workload into smaller jobs and run those in parallel thus drastically reducing execution time. These are some example scenarios:
- In Visual Effects, we cover this in this Rendering workshop: AWS Batch provides content producers and post-production houses with tools to automate content rendering workloads and reduces the need for human intervention due to execution dependencies or resource scheduling.
- Media supply chain: AWS Batch simplifies complex media supply chain workflows by coordinating the execution of disparate and dependent jobs at different stages of processing, and supports a common framework for managing content preparation for different contributors to the media supply chain.
- In life-sciences: Drug screening. AWS Batch allows research scientists involved in drug discovery to more efficiently and rapidly search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor or enzyme.
- In Finance, Post-trade analytics: trading desks require batch processing of large data sets to constantly analyze day’s transaction costs and execution reporting, among other areas. AWS Batch enables the automation of these workloads so that you can understand the pertinent risk going into the next day’s trading cycle and make better decisions based on data.