Spot Placement Score (SPS)
 Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Launching EC2 Spot Instances.
Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Launching EC2 Spot Instances.
As Spot capacity fluctuates, you can’t be sure that you’ll always get the capacity that you need. The Spot placement score feature can recommend an AWS Region(s) or Availability Zone(s) where you can run the workload based on your Spot capacity requirements. The Spot placement score gives the Region(s) or Availability Zone(s) a score of 1 to 10 indicating how likely a Spot request will succeed. A score of 10 indicates that your Spot request is highly likely—but not guaranteed—to succeed, and a score of 1 indicates that your Spot request is not likely to succeed at all. For SPS to return a meaningful score, the SPS request must be configured with at least three instance types.
You can calculate a Spot placement score by using the Amazon EC2 console or the AWS CLI.
The same Spot placement score request can yield different scores for the same Regions or Availability Zones when calculated at different times. The same Spot placement score might be returned for different Regions or Availability Zones.
Spot placement score can be used to
- determine the ability to relocate and scale Spot compute capacity in a different region if the workload is region flexible
- identify the most optimal Availability Zone to run the single Availability Zone workloads
- find an optimal configuration that will fulfill the Spot capacity needs
Using Amazon EC2 console to calculate Spot placement score
- Open the Amazon EC2 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/.
- In the navigation pane, choose Spot Requests.
- Choose Spot placement score in the top right corner.
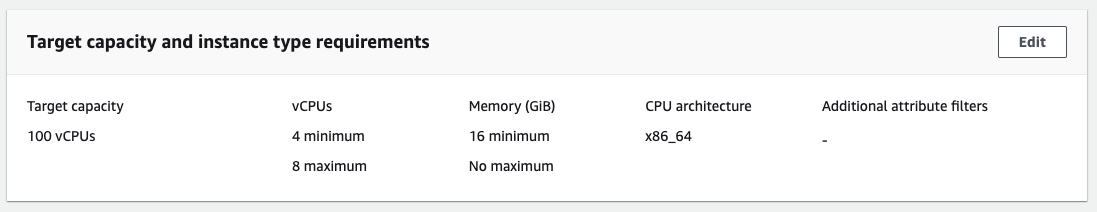
Provide the inputs as show below:
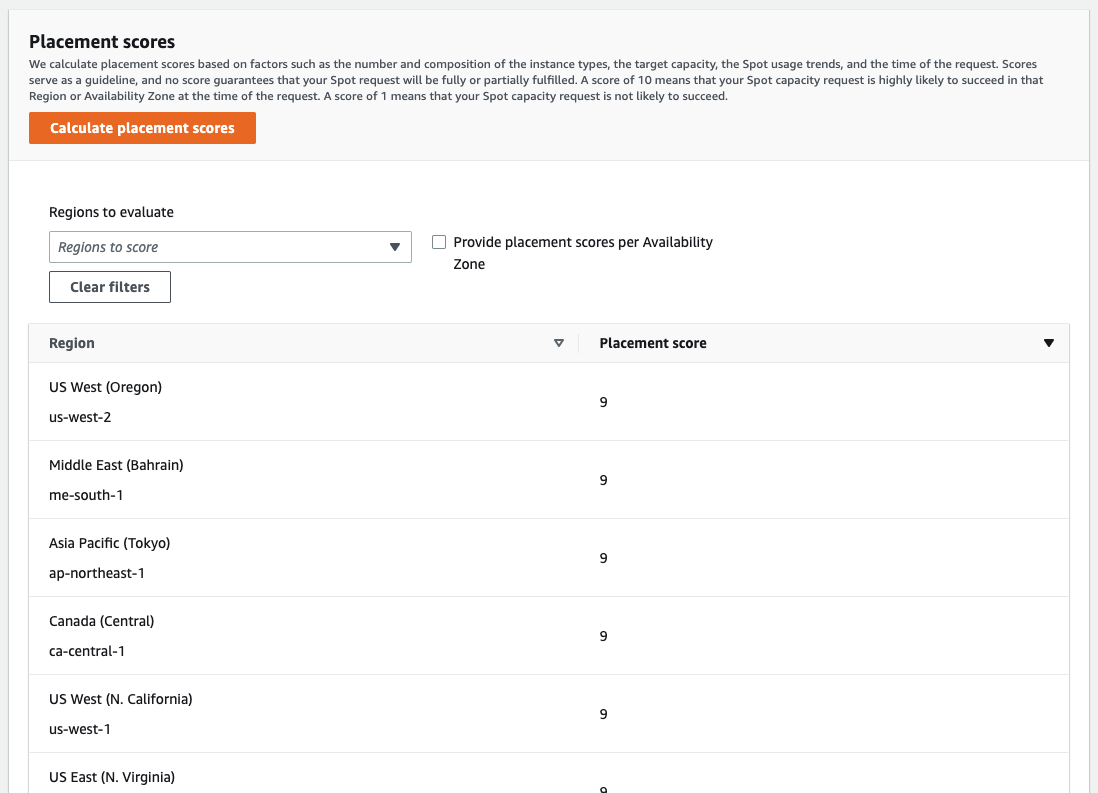
A sample output of the response on the console is show below:
Using AWS CLI to calculate Spot placement score
You can use a json file that includes the parameters for running a Spot placement score request.
To get started, specify the target Spot capacity, as vCPUs or memory in MiB or in units. By specifying your target capacity in terms of the number of vCPUs or the amount of memory, you can use these units when counting the total capacity. For example, when mixing instances of different sizes, you can specify the target capacity in terms of total memory. Instances of different sizes are considered based on its memory rather than total number of instances when totaling up the target capacity.
Specify instance attributes or instance types. If instances can be selected based on attributes, you can use attribute-based instance type selection to specify your compute needs. If you need to use specific instances types for your workload, specify these instance types. In both cases, ensure that your request for Spot capacity includes at least a minimum of three instance types in the request.
cat <<EoF > ./sps-input.json
{
"InstanceRequirementsWithMetadata": {
"ArchitectureTypes": [
"x86_64"
],
"InstanceRequirements": {
"VCpuCount": {
"Min": 4,
"Max": 8
},
"MemoryMiB": {
"Min": 16384
}
}
},
"TargetCapacity": 100,
"TargetCapacityUnitType": "vcpu",
"SingleAvailabilityZone": false
}
EoF
In the above example, we will be running a Spot placement score for 10K vCPUs using any x86 architecture instance which has a vCPU between 4 and 8 and Memory greater than 16MB. To run the Spot placement score request with the above parameters, use this command.
aws ec2 get-spot-placement-scores --cli-input-json file://./sps-input.json
Spot placement score returns the top 10 regions or top 10 Availability Zones where the specific Spot request is most likely to succeed. You can narrow down the Regions to be considered in the response. You can combine the Region filter and a request for scored Availability Zones to return a scored list of all of the Availability Zones.
Challenges
Given the configuration you used above, try to answer the following questions. Click to expand and see the answers.
The Spot placement scores might differ in different regions. A sample response for the request is shown below. Note the Score for the region which is between a 1 and 10.
{
"SpotPlacementScores": [
{
"Region": "ap-southeast-2",
"Score": 8
},
{
"Region": "ap-south-1",
"Score": 6
},
{
"Region": "us-east-1",
"Score": 9
},
{
"Region": "eu-west-2",
"Score": 6
},
{
"Region": "us-west-2",
"Score": 9
},
{
"Region": "ap-northeast-1",
"Score": 7
},
{
"Region": "eu-west-1",
"Score": 9
},
{
"Region": "ap-northeast-2",
"Score": 6
},
{
"Region": "us-east-2",
"Score": 9
},
{
"Region": "ap-southeast-1",
"Score": 8
}
]
}
To create an Spot placement score input request with certain regions, you can use RegionNames filter as shown in the json file below. This example uses us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-1, and us-west-2 regions.
cat <<EoF > ./sps-input.json
{
"InstanceRequirementsWithMetadata": {
"ArchitectureTypes": [
"x86_64"
],
"InstanceRequirements": {
"VCpuCount": {
"Min": 4,
"Max": 8
},
"MemoryMiB": {
"Min": 16384
}
}
},
"TargetCapacity": 100,
"TargetCapacityUnitType": "vcpu",
"SingleAvailabilityZone": false,
"RegionNames": [
"us-east-1",
"us-east-2",
"us-west-1",
"us-west-2"
]
}
EoF
To run the request, use the command:
aws ec2 get-spot-placement-scores --cli-input-json file://./sps-input.json
To create an Spot placement score input request at the Availability Zones level, set the SingleAvailabilityZone parameter to true, as shown in the configuration below.
cat <<EoF > ./sps-input.json
{
"InstanceRequirementsWithMetadata": {
"ArchitectureTypes": [
"x86_64"
],
"InstanceRequirements": {
"VCpuCount": {
"Min": 4,
"Max": 8
},
"MemoryMiB": {
"Min": 16384
}
}
},
"TargetCapacity": 100,
"TargetCapacityUnitType": "vcpu",
"SingleAvailabilityZone": true
}
EoF
To run the request, use the command:
aws ec2 get-spot-placement-scores --cli-input-json file://./sps-input.json
To create an Spot placement score input request using specific instance types, use the json below that includes instance types - .
cat <<EoF > ./sps-input.json
{
"InstanceTypes": [
"m6i.xlarge",
"m6i.2xlarge",
"m6a.xlarge",
"m6a.2xlarge",
"m5.xlarge",
"m5.2xlarge",
"m5a.xlarge",
"m5a.2xlarge"
],
"TargetCapacity": 100,
"TargetCapacityUnitType": "vcpu",
"SingleAvailabilityZone": false
}
EoF
To run the request, use the command:
aws ec2 get-spot-placement-scores --cli-input-json file://./sps-input.json
Optional reads
You can learn more about spot placement score by reading the launch blog post.