Launch a cluster - Step 2
 Please note: That this workshop has been deprecated. For the latest and updated version featuring the newest features, please access the Workshop at the following link: Cost efficient Spark applications on Amazon EMR.
This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before, or those who want to reference this workshop for earlier version.
Please note: That this workshop has been deprecated. For the latest and updated version featuring the newest features, please access the Workshop at the following link: Cost efficient Spark applications on Amazon EMR.
This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before, or those who want to reference this workshop for earlier version.
Step 2: Hadware
-
Under Cluster Composition » Instance group configuration, select Instance fleets.
-
Under Network, select the VPC that you deployed using the CloudFormation template earlier in the workshop (or the default VPC if you’re running the workshop in an AWS event), and select all subnets in the VPC.
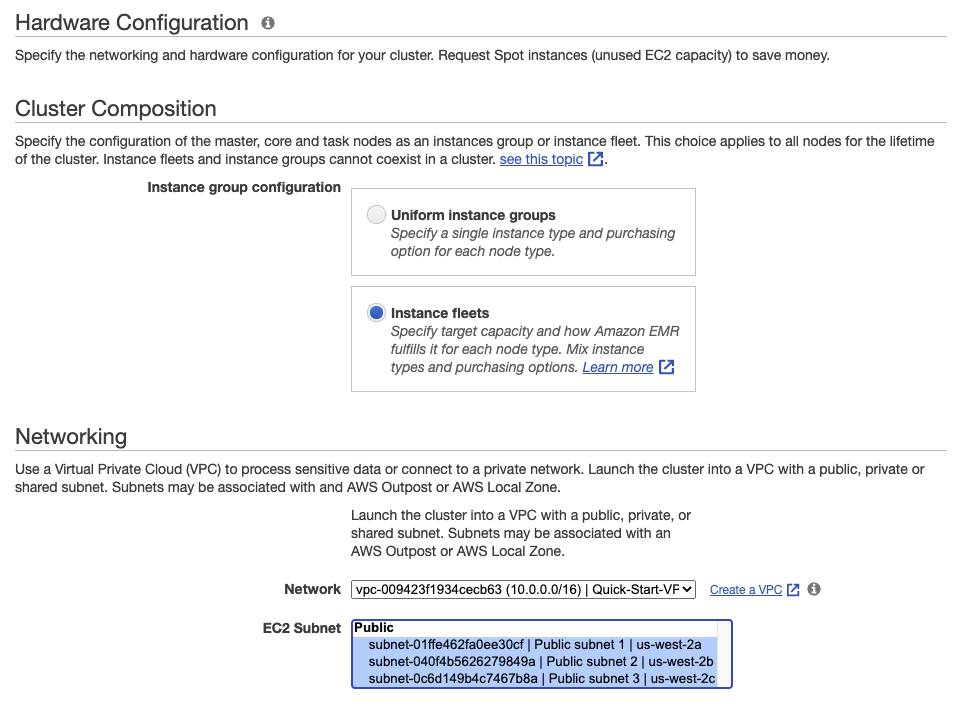
We recommend that you provide a list of subnets (Availability Zones) and instance types in instance fleets, Amazon EMR will automatically select one optimal subnet (AZ) based on cost and availability of instance types.
- Click on the checkbox Apply allocation strategy to leverage lowest-priced allocation strategy for On-Demand Instances and capacity-optimized allocation strategy for Spot Instances. Allocation strategy will also allow you to configure up to 15 instance types on the Task Instance fleet in the EMR console and up to 30 instance types when you create the cluster with AWS CLI or EMR API.

Cluster Nodes and Instances
Master fleet
The master node does not typically have large computational requirements. For clusters with a large number of nodes, or for clusters with applications that are specifically deployed on the master node (JupyterHub, Hue, etc.), a larger master node may be required and can help improve cluster performance. For example, consider using a General Purpose m5.xlarge instance for small clusters (50 or fewer nodes), and increasing to a larger instance type for larger clusters.
You may experience insufficient capacity when using On-Demand Instances with allocation strategy for instance fleets. We recommend specifying a larger number of instance types for On-Demand Instances also, to diversify and reduce the chance of experiencing insufficient capacity.
Under Node type » Master, click Add / remove instance types to fleet and select General Purpose instance types - i.e m4.xlarge, m5.xlarge, m5a.xlarge and m5d.xlarge. EMR will only provision one instance, but will select the cheapest On-Demand instance type for the Master node from the given instance types.
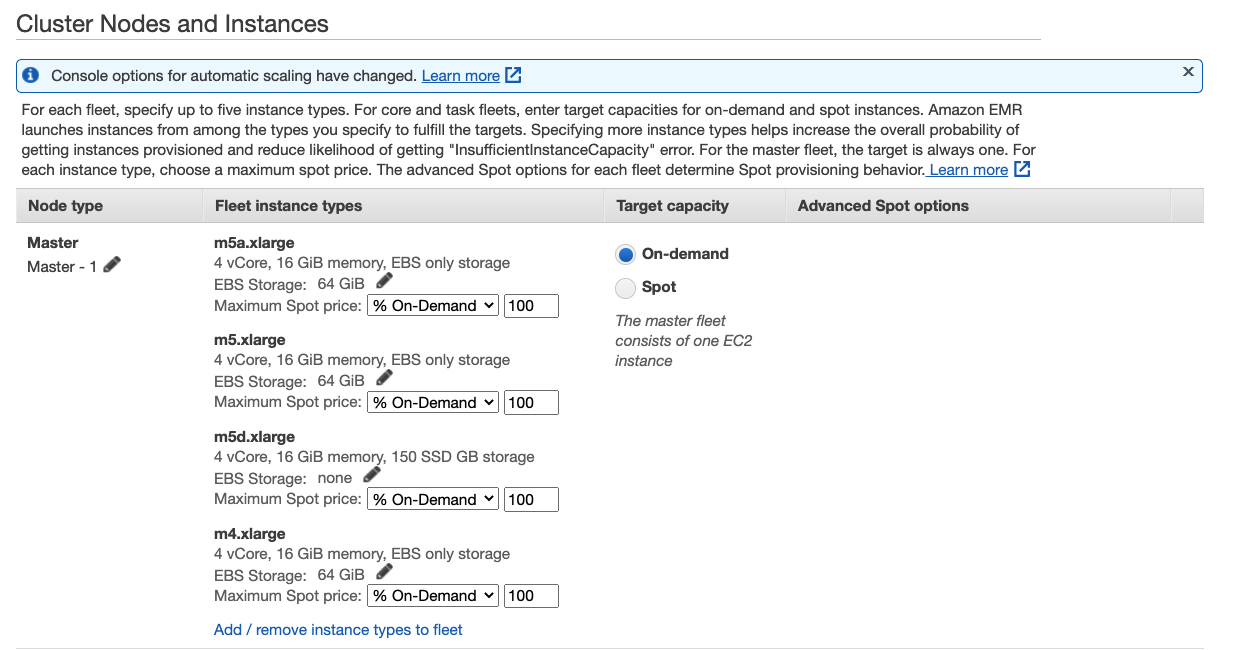
Unless your cluster is very short-lived and the runs are cost-driven, avoid running your Master node on a Spot Instance. We suggest this because a Spot interruption on the Master node terminates the entire cluster. If you want to dive deeper into when to use On-Demand and Spot in your EMR clusters, click here
Core fleet
When using EMR instance fleets, one core node is mandatory. Since you don’t use HDFS in this workshop, you will auto-scale task fleet and keep only one mandatory core node using On-Demand Instances. Specify 4 On-demand units, to allow single core node to run one executor and YARN application master.
Under the Node type » Core , click Add / remove instance types to fleet and select five instance types that you noted before as suitable to run an executor (given the 18G executor size), for example:
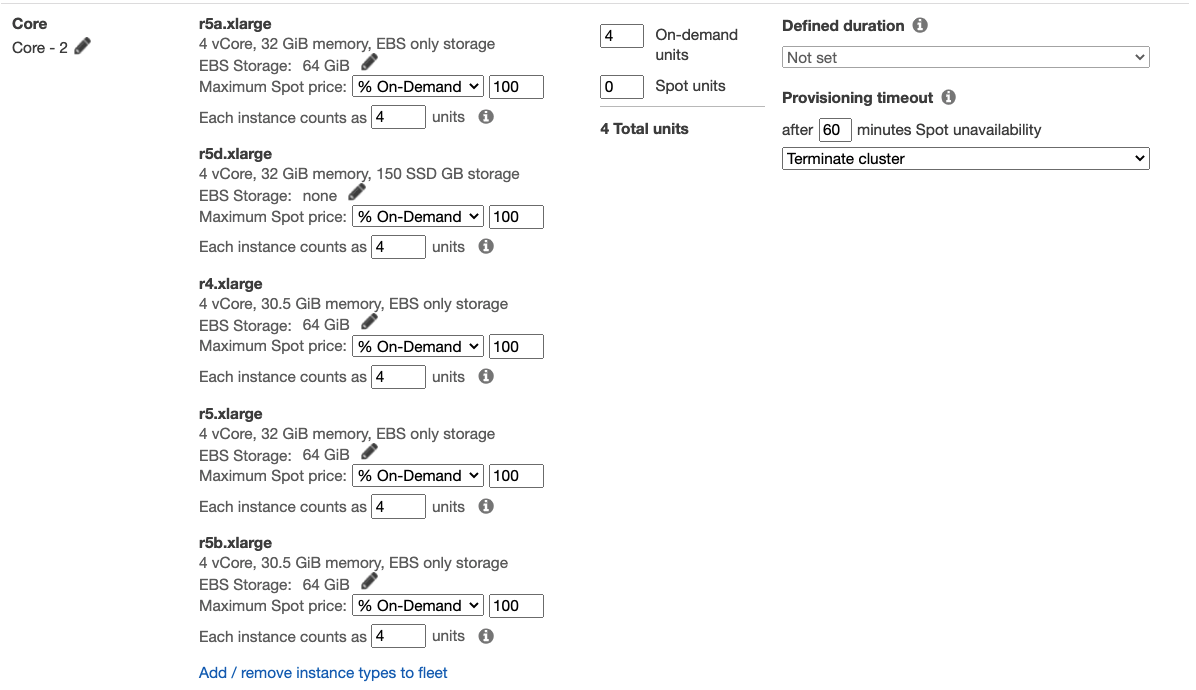
Core nodes process data and store information using HDFS, terminating a core instance risks data loss. YARN application master runs on one of the core nodes, in case of Spark applications the Spark driver runs on the YARN application master container hosted on the core node. Spark driver is a single point of failure in Spark applications. If driver dies, all other linked components will be discarded as well.
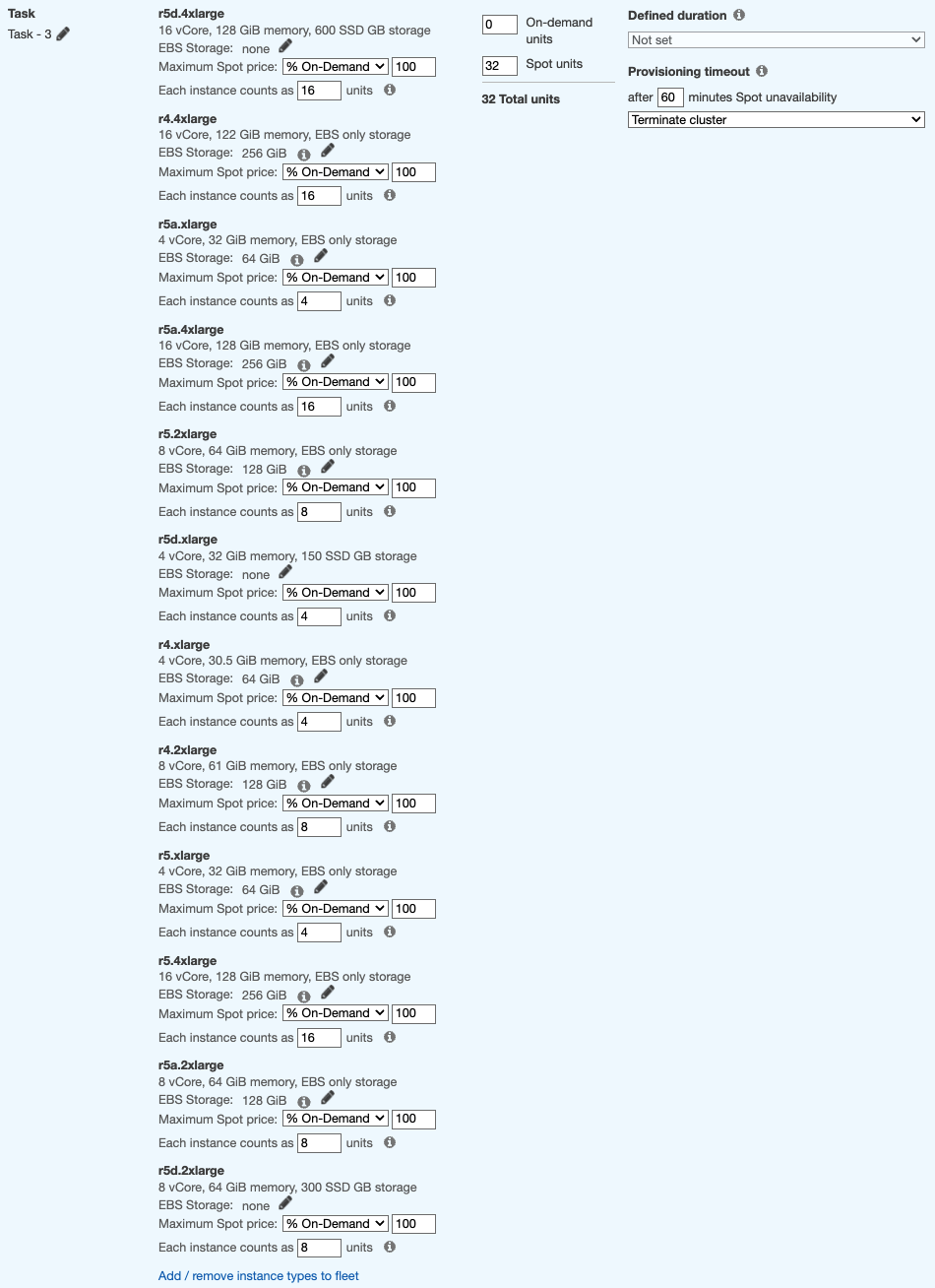
Task fleet
Task nodes run only Spark executors and no HDFS DataNodes, therefore task nodes are a great fit for scaling out and increasing parallel executions to achieve faster execution times.
Under the Node type » Task , click Add / remove instance types to fleet and select up to 15 instance types you noted before as suitable for your executor size. Since the executor size is 4 vCore, let’s specify 32 Spot units in order to run 8 executors to start with.
Enabling cluster scaling
While you can always manually adjust the number of core or task nodes (EC2 instances) in your Amazon EMR cluster, you can also use the power of EMR auto-scaling to automatically adjust the cluster size in response to changing workloads without any manual intervention.
Let’s enable scaling for this cluster using Amazon EMR Managed Scaling. With EMR Managed scaling you specify the minimum and maximum compute limits for your cluster and Amazon EMR automatically resizes EMR clusters for best performance and resource utilization. EMR Managed Scaling constantly monitors key metrics based on workload and optimizes the cluster size for best resource utilization
EMR Managed Scaling is supported for Apache Spark, Apache Hive and YARN-based workloads on Amazon EMR versions 5.30.1 and above.
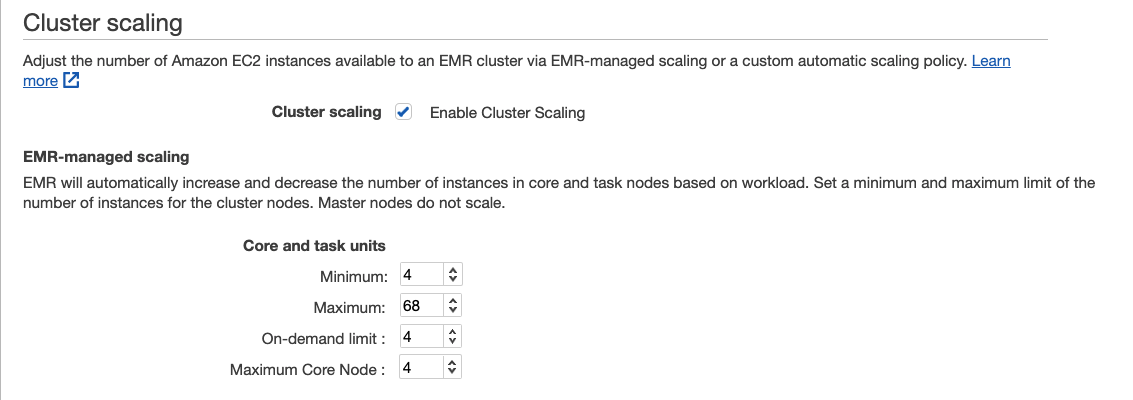
- Select the checkbox for Enable Cluster Scaling in Cluster scaling section.
- Set MinimumCapacityUnits to 4, when cluster is not running any jobs you can allow it to scale down the task fleet to 0 and keep only the single core node that equals to 4 On-Demand units.
- Set MaximumCapacityUnits to 68, you start the cluster with a core fleet with a single node (4 On-Demand units) and a task fleet with 32 Spot units. You can allow EMR to further scale out the task fleet to twice the initial size (64 Spot units) and keep the core fleet as is. Therefore, MaximumCapacityUnits equals to 4 units of core nodes + 64 units of tasks nodes = 68 units.
- Set MaximumOnDemandCapacityUnits to 4, allowing only core nodes to run on On-demand Instances.
- Set MaximumCoreCapacityUnits to 4, allowing only a single core nodes and scale out using task nodes.
Managed Scaling now also has the capability to prevent scaling down instances that store intermediate shuffle data for Apache Spark. Intelligently scaling down clusters without removing the instances that store intermediate shuffle data prevents job re-attempts and re-computations, which leads to better performance, and lower cost. Click here for more details.
click Next to continue to the next steps of launching your EMR cluster.