Scaling your application faster
 Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Efficient and Resilient Workloads with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Efficient and Resilient Workloads with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
Warm pools
A warm pool is a pool of pre-initialized EC2 instances that sits alongside an Auto Scaling group. Whenever your application needs to scale out, gives you the ability to decrease latency for your applications that have exceptionally long boot times.
Set the warm pool size:
It’s important to decide how to set the warm pools size as it will make huge difference in associated cost. Plan a minimum and a maximum boundaries for the warm pool:
- By default and in this step, warm pool size is the difference between the number of currently running instances and the maximum capacity.
- However if you’re running a large Auto Scaling group that won’t be the best cost optimized option, in that case you can set a maximum prepared capacity which counts current running instances as part of it.
- You can also set a static number as the minimum pool size to ensure that there is always at least a certain number of warmed instances (regardless of the number of running instances) available to react to demand spikes.
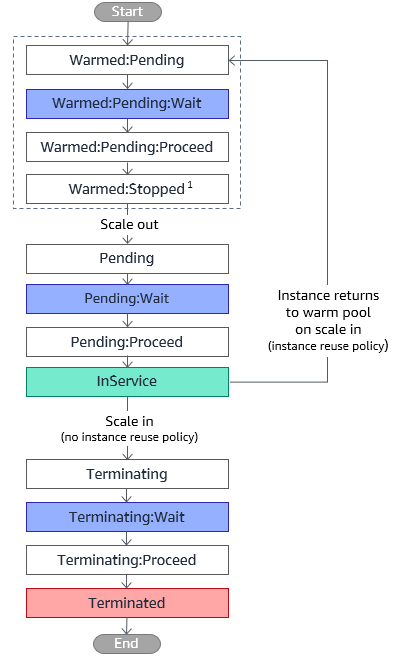
You can keep instances in the warm pool in one of three states: Stopped, Running, or Hibernated (if supported by the instance type). Keeping instances in a Stopped state is an effective way to minimize costs. With stopped instances, you pay only for the volumes that you use and the Elastic IP addresses attached to the instances.
By default when ASG scales in instances it get terminated but in warm pools, you can configure reuse policy to return instances to warm pool.
Limitations: You cannot add a warm pool to Auto Scaling groups that have a mixed instances policy or that launch Spot Instances.
Add warm pools to the Auto Scaling group
In this step, you add a warm pool to your Auto Scaling group to pre-initialize your instances, so that instances can be brought into service more rapidly.
You want to keep your warm pool instances in a stopped state after they have completed their initialization actions. You will set the optional warm pool sizing parameters --min-size to 2 and leave --max-group-prepared-capacity empty. This means that this warm pool has a minimum size of 2 and a maximum prepared capacity equal to the max size of the Auto Scaling group. The maximum prepared capacity includes instances launched into the Auto Scaling group, and instances launched into the warm pool.
aws autoscaling put-warm-pool --auto-scaling-group-name "ec2-workshop-asg" --pool-state Stopped --min-size 2
Now let’s check the warm pool in the AWS Console
- Navigate to the Auto Scaling console, click on Auto Scaling group
ec2-workshop-asg - Click on tab Instance management
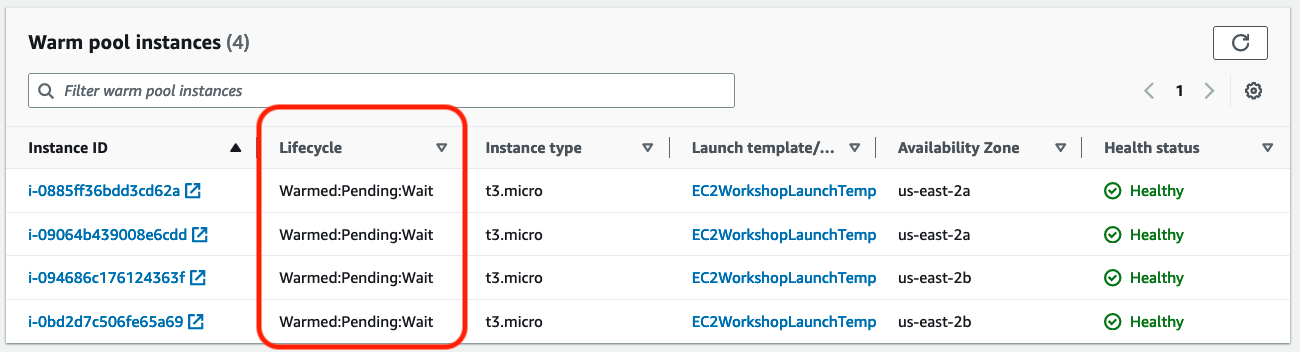
- A warm pool has been created and the instances have started initiating, note the current lifecycle for the instances is Warmed:Pending:Wait
- Once the instances are initialized, the lifecycle will be changed to Warmed:Stopped