Introduction to ECS

-
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run and scale containerized applications on AWS.
-
Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install and operate your own container orchestration software, manage and scale a cluster of virtual machines, or schedule containers on those virtual machines.
-
ECS is also deeply integrated into the rest of the AWS ecosystem.
Amazon ECS Clusters
An Amazon ECS cluster is a logical grouping of tasks or services, which we’ll cover in more detail in the following pages.
- If you are running tasks or services that use the EC2 launch type, a cluster is also a grouping of container instances.
- If you are using capacity providers, a cluster is also a logical grouping of capacity providers.
- A cluster can be a combination of Fargate and EC2 launch types.
When you first use Amazon ECS, a default cluster is created for you, but you can create multiple clusters in an account to keep your resources separate.
For more information on ECS Clusters, see here.
Tasks Definitions
To prepare your application to run on Amazon ECS, you create a task definition. The task definition is a text file, in JSON format, that describes one or more containers, up to a maximum of ten, that form your application.
We can think of it as a blueprint for your application. Task definitions specify various parameters for your application. Examples of task definition parameters are which containers to use, which launch type to use, which ports to open for your application, and what data volumes to use with the containers in the task. The specific parameters available for the task definition depend on which launch type you are using. For more information about creating task definitions, see Amazon ECS Task Definitions.
The following is an example of a task definition containing a single container that runs an NGINX web server using the Fargate launch type. For a more extended example showing the use of multiple containers in a task definition, see Example Task Definitions.
{
“family”: “webserver”,
“containerDefinitions”: [
{
“name”: “web”,
“image”: “nginx”,
“memory”: “100”,
“cpu”: “99”
},
],
“requiresCompatibilities”: [
“FARGATE”
],
“networkMode”: “awsvpc”,
“memory”: “512”,
“cpu”: “256”,
}
Fargate
AWS Fargate is a technology for Amazon ECS that allows you to run containers without having to manage servers or clusters. With AWS Fargate, you no longer have to provision, configure, and scale clusters of virtual machines to run containers. This removes the need to choose server types, decide when to scale your clusters, or optimize cluster packing. AWS Fargate removes the need for you to interact with or think about servers or clusters. Fargate lets you focus on designing and building your applications instead of managing the infrastructure that runs them.
Tasks and Scheduling
A task is the instantiation of a task definition within a cluster. After you have created a task definition for your application within Amazon ECS, you can specify the number of tasks that will run on your cluster. Each task that uses the Fargate launch type has its own isolation boundary and does not share the underlying kernel, CPU resources, memory resources, or elastic network interface with another task.
The Amazon ECS task scheduler places tasks within your cluster. There are several scheduling options available. For example, you can define a service that runs and maintains a specified number of tasks simultaneously. You might also want to run a single task on a schedule or invoke it through APIs or as part of a serverless workflow. For more information about the different scheduling options available, see Scheduling Amazon ECS Tasks.
Services
Amazon ECS allows you to run and maintain a specified number of instances of a task definition simultaneously in an Amazon ECS cluster. This is called a service. If any of your tasks should fail or stop for any reason, the Amazon ECS service scheduler launches another instance of your task definition to replace it and maintain the desired count of tasks in the service depending on the scheduling strategy used.
Besides maintaining the desired count of tasks in your service, you can optionally run your service behind a load balancer. The load balancer distributes traffic across the tasks associated with the service.
There are two service scheduler strategies available:
-
REPLICA:
- The replica scheduling strategy places and maintains the desired number of tasks across your cluster. By default, the service scheduler spreads tasks across Availability Zones. You can use task placement strategies and constraints to customize task placement decisions. For more information, see Replica.
-
DAEMON:
- The daemon scheduling strategy deploys exactly one task on each active container instance that meets all the task placement constraints that you specify in your cluster. The service scheduler evaluates the task placement constraints for running tasks and will stop tasks that do not meet the placement constraints. When using this strategy, there is no need to specify a desired number of tasks, a task placement strategy, or use Service Auto Scaling policies. For more information, see Daemon.
Service Discovery
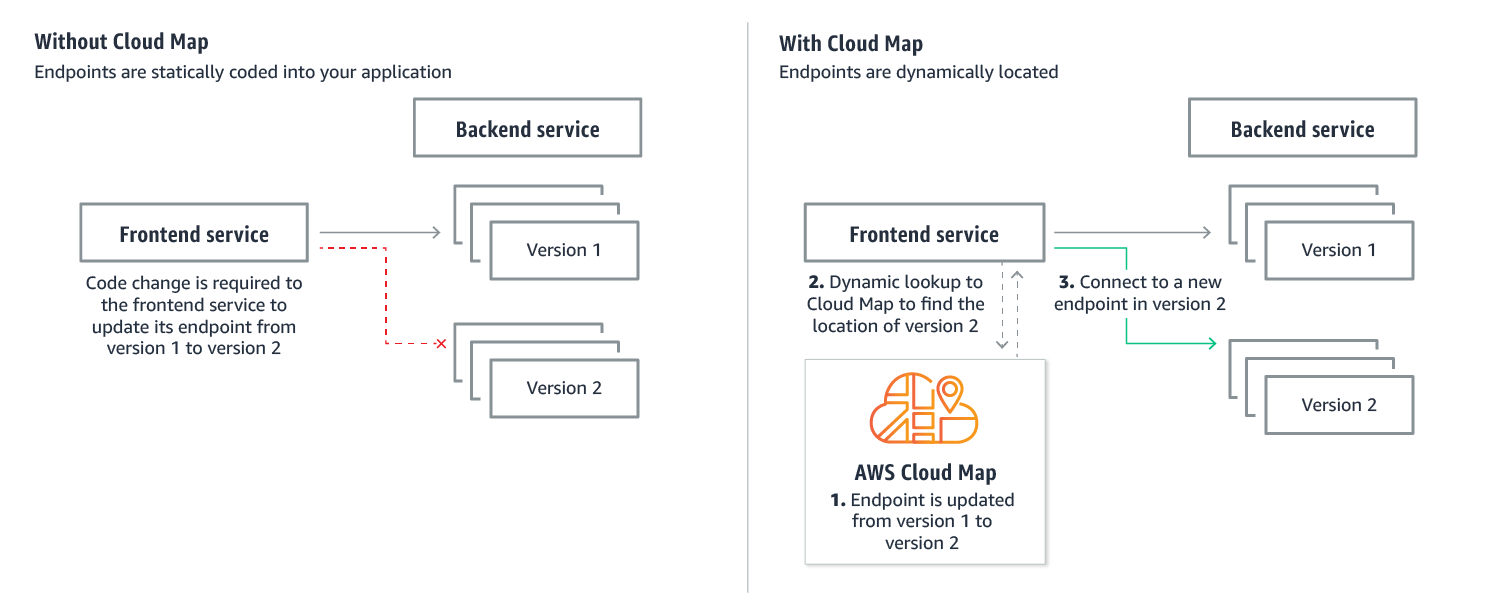
Because containers are immutable by nature, they can churn regularly and be replaced with newer versions of the service. This means that there is a need to register the new and deregister the old/unhealthy services. To do this on your own is challenging, hence the need for service discovery.
AWS Cloud Map is a cloud resource discovery service. With Cloud Map, you can define custom names for your application resources, and it maintains the updated location of these dynamically changing resources. This increases your application availability because your web service always discovers the most up-to-date locations of its resources.
Cloud Map natively integrates with ECS, and as we build services in the workshop, will see this firsthand. For more information on service discovery with ECS, please see here.