Create an ECS cluster
Let us first create an empty ECS cluster.To create an ECS cluster, follow these steps:
- Open the ECS console in the region where you are looking to launch your cluster.
- Click Create Cluster
- Un-select New ECS Experience on the top left corner to work on previous ECS console version (Capacity providers not supported on new version)
- Under Select cluster template select EC2 Linux + Networking
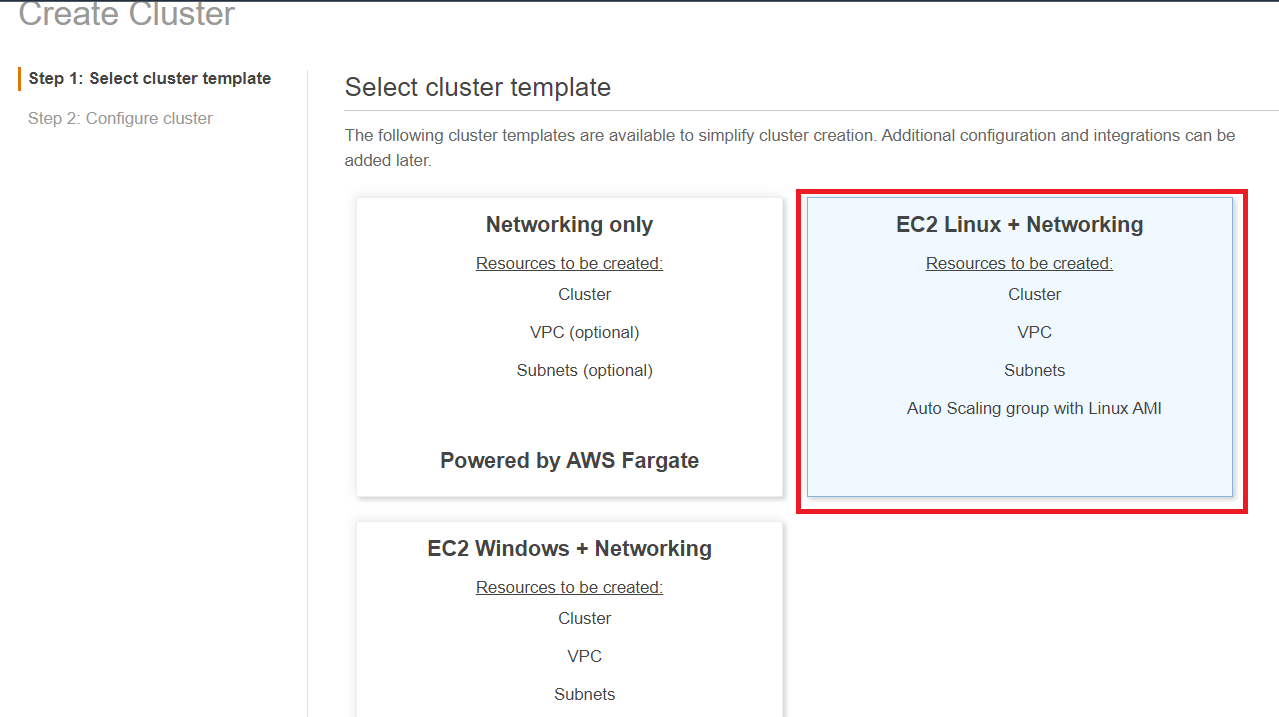
- Click Next step
- Under Configure cluster for Cluster name, enter EcsSpotWorkshop
- Select the checkbox Create an empty cluster
- Select the checkbox Enable Container Insights
If you are using a different name for the cluster than EcsSpotWorkshop, please make sure you update the Launch template ecs agent bootstrapping. Learn more about ECS agent bootstrapping [here] (#ecs-agent-bootstrapping)
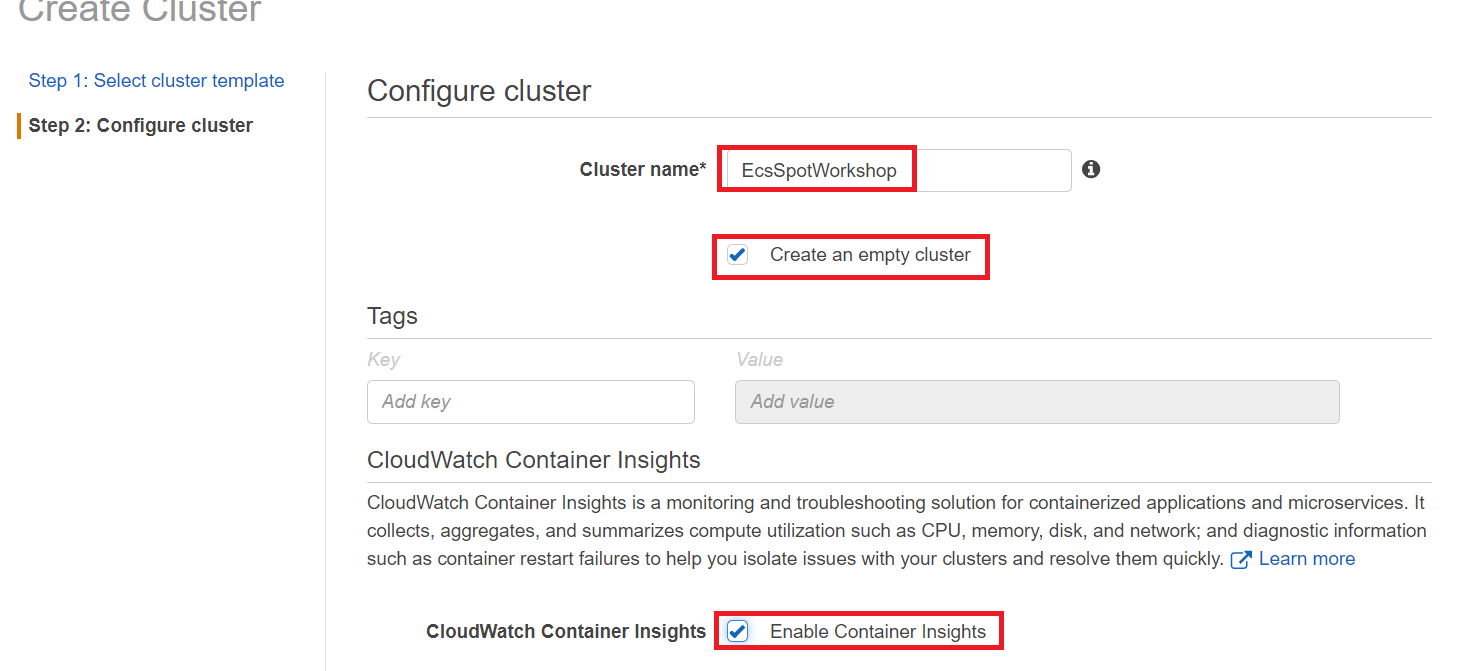
- Click Create
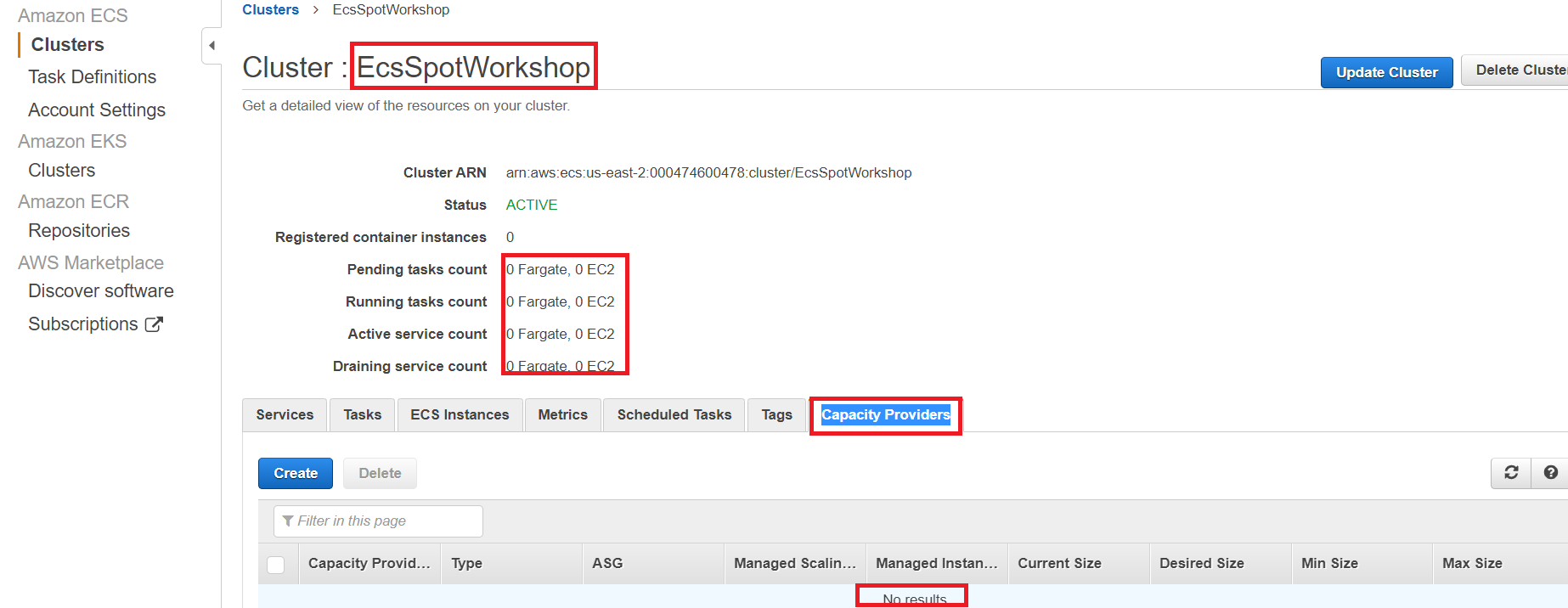
- Click View Cluster
- Click Capacity Providers tab
The new ECS cluster will appear as below in the AWS Console.
CloudWatch Container Insights collects, aggregates, and summarizes metrics and logs from your containerized applications and microservices. It collects metrics for many resources, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network. Container Insights is available for Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), and Kubernetes platforms on Amazon EC2. Amazon ECS support includes support for Fargate. You can read more about CloudWatch Container Insights here.
Launch Templates & ECS Agent Bootstrapping
Launch Template User Data section is key in ECS for actions such as bootstrapping container instances and configuring the ECS agent
EC2 launch templates reduce the number of steps required to create an instance by capturing all launch parameters within one resource. For example, a launch template can contain the ECS optimized AMI, instance type, User data section, Instance Profile / Role, and network settings that you typically used to launch instances. When you launch an instance using the Amazon EC2 console, an AWS SDK, a CLI tool, or an EC2 Auto Scaling group (like we will use in this workshop), you can specify the launch template to use.
In this case we have pre-created an EC2 launch template when we deployed the CloudFormation stack. You can use the AWS Management Console to see the configuration. Please note that launch templates are necessary in order to use EC2 Auto Scaling groups with mixed instances policy (to allow for mixing On-Demand and Spot Instances in an Auto Scaling group, and diversifying the instance type selection).
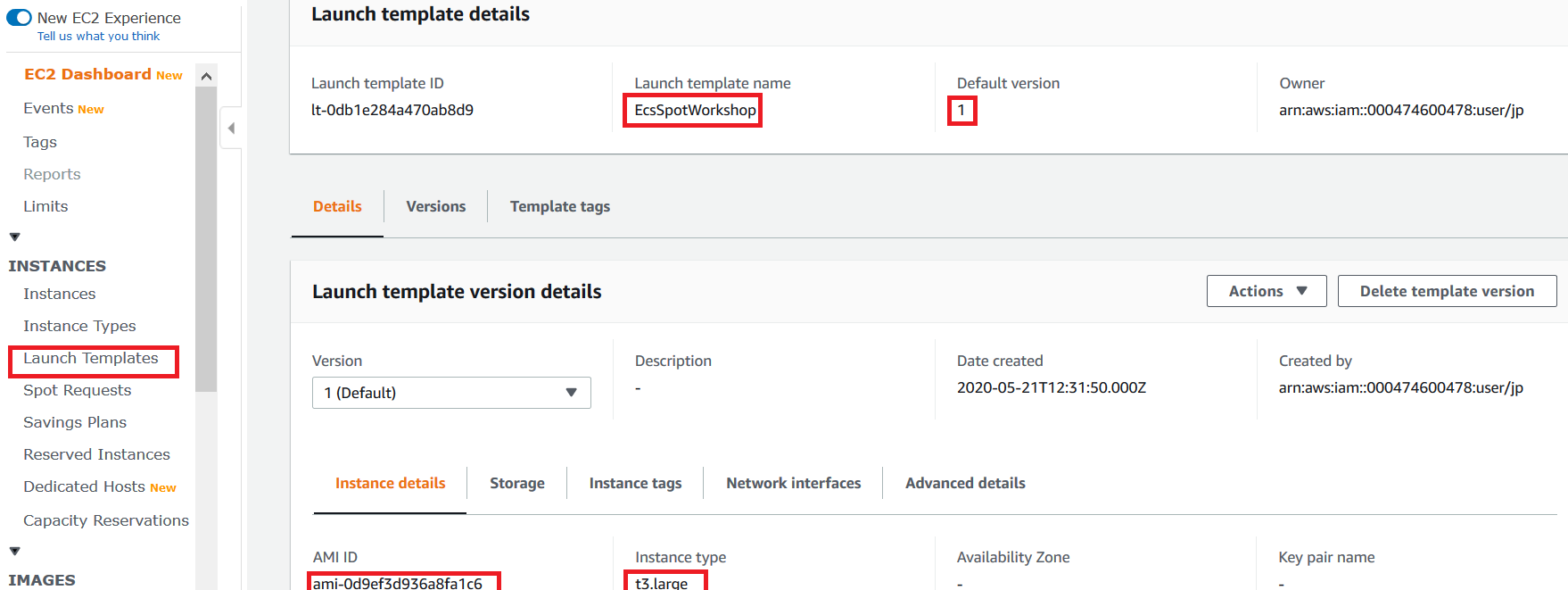
Select launch template and navigate to Advanced Details tab. Review the user data section of the EC2 launch template to see ECS Container agent configuration.
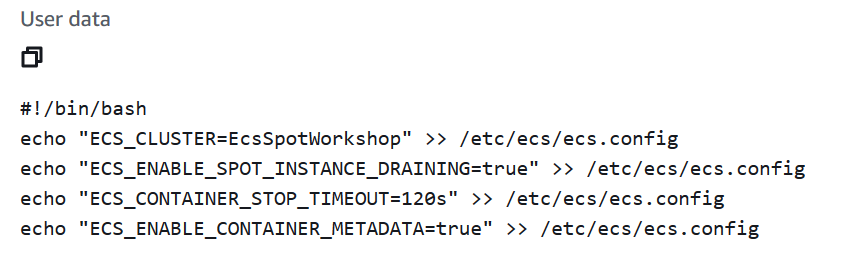
-
ECS_CLUSTER: The cluster that will be used by the ECS Agent to bootstrap against and connect. Must match a name of an ECS Cluster.
-
ECS_CONTAINER_STOP_TIMEOUT: Time to wait from when a task is stopped before its containers are forcefully stopped if they do not exit normally on their own
-
ECS_ENABLE_SPOT_INSTANCE_DRAINING: Whether to enable Spot Instance draining for the container instance. When true, if the container instance receives a Spot interruption notice, then the agent sets the instance status to DRAINING, which gracefully shuts down and replaces all tasks running on the instance that are part of a service.
-
ECS_ENABLE_CONTAINER_METADATA: When true, the agent creates a file describing the container’s metadata. The file can be located and consumed by using the container environment variable $ECS_CONTAINER_METADATA_FILE