Workflow orchestration
You have now all the AWS Batch components in place, and are ready to start submitting jobs that will be placed in a queue and processed by a compute environment when AWS Batch’s scheduler starts running them. We are going to use AWS Step Functions to orchestrate the execution of our risk pipeline, from pre-processing the portfolio, to merging the resulting PVs.
AWS Step Functions helps you orchestrate your AWS Batch jobs using serverless workflows, called state machines. You can use Step Functions to orchestrate preprocessing of data and Batch to handle the large compute executions, providing an automated, scalable, and managed batch computing workflow. The CloudFormation template has created the following state machine:
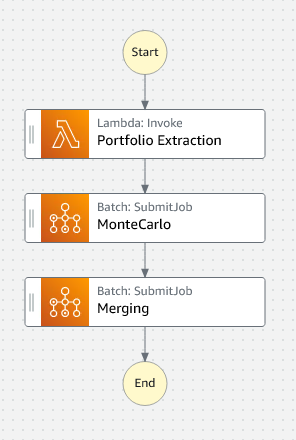
You will notice that each step in the pipeline has been mapped to a state. In AWS Step Functions, you can create state machines using the Amazon States Language or the AWS Step Functions Workflow Studio.
The script needs: (a) the location of the portfolio.json file, (b) the location where results will be uploaded, (c) the Job Definition that will be used to submit the job, (d) the Job Queue where it will be placed and (e) the name that will be used to submit it.
The state machine will:
- Run an AWS Lambda function to download the portfolio.json file from S3 to determine how many positions are in the portfolio.
- Submit a Batch array job that will run our Autocallable pricing code to PV each position.
- Run an AWS Lambda function to collate the individual position results into an aggregate file.
To start the process, perform the following api call to pass a payload to the state machine with the job name, input path, output path, ARNs of the Job Definition and Job queue for AWS Batch to use:
export JOB_NAME="MCAutocallable"
export EXECUTION_ARN=$(aws stepfunctions start-execution --state-machine-arn "${StateMachineArn}" --input "{\"jobName\": \"${JOB_NAME}\", \"inputUri\": \"s3://${BucketName}/${MonteCarloFileName}\", \"outputUri\": \"s3://${BucketName}/${JOB_NAME}\", \"jobDefinitionArn\": \"${JOB_DEFINITION_ARN}\", \"jobQueueArn\": \"${JOB_QUEUE_ARN}\"}" | jq -r '.executionArn')
echo "State machine started. Execution Arn: ${EXECUTION_ARN}."
To learn more about this API, see start-execution CLI Command Reference. At this point the state machine is started and you are ready to monitor the progress of the pipeline.