Launch From Warm Pool
 Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Efficient and Resilient Workloads with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Efficient and Resilient Workloads with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
Measure the launch speed of instances launched from warm pool into an Auto Scaling group
Now that you have pre-initialized instances in the warm pool, you can scale your Auto Scaling group and launch a pre-initialized instance rather than launching a new instance that has not been pre-initialized.
Increase desired capacity
Let’s increase the desired capacity of your Auto Scaling group to 2 instances.
aws autoscaling set-desired-capacity --auto-scaling-group-name "ec2-workshop-asg" --desired-capacity 2
Observe warm pool change
Now, let’s describe the warm pool and observe changes. As you can see below, the additional instance you just launched is no longer in the warm pool. It was launched from the warm pool into the Auto Scaling group in response to your increase in desired capacity.
aws autoscaling describe-warm-pool --auto-scaling-group-name "ec2-workshop-asg" | jq -r '.Instances[]| "\(.InstanceId)\t\(.LifecycleState)"'
i-0851feaba1df1fcc5 Warmed:Stopped
i-0d3f75c968995f1dc Warmed:Stopped
i-0e6f840558778cbd4 Warmed:Stopped
Measure launch speed
Let’s measure how long did that instance take to be ready as it moved from the warm pool to the Auto Scaling group.
activities=$(aws autoscaling describe-scaling-activities --auto-scaling-group-name "ec2-workshop-asg" | jq -r '.Activities[0]') && \
start_time=$(date -d "$(echo $activities | jq -r '.StartTime')" "+%s") && \
end_time=$(date -d "$(echo $activities | jq -r '.EndTime')" "+%s") && \
activity=$(echo $activities | jq -r '.Description') && \
echo $activity Duration: $(($end_time - $start_time))"s" || echo "Current activity is still in progress.."
As you can see from the following results, because the instance was pre-initialized, the instance launch duration was significantly reduced. This means you can now more rapidly place instances into service in response to load placed on your workload by launching pre-initialized instances from the warm pool. Making your application more resilient and responsive to spike demands.
Launching a new EC2 instance from warm pool: i-0ea10fdc59a07df6e Duration: 36s
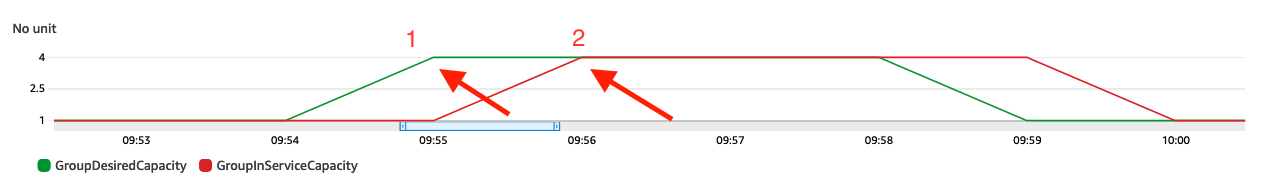
Since you have enabled the CloudWatch metrics collection for the Auto Scaling group, let’s compare the capacity metrics before and after enabling warm pools.
- Navigate to Amazon CloudWatch Console.
- From left side navigation, click on Metrics then All metrics.
- In the Browse tab select Auto Scaling under AWS namespaces
- Select Group Metrics, then select these two metrics GroupDesiredCapacity and GroupInServiceCapacity attached with ec2-workshop-asg. This should add the metrics to the graph.
- Switch to Graphed metrics tab and change granularity Period to 1 minute for both metrics.
- Note the difference in time between DesiredCapacity and InServiceCapacity before and after enabling warm pools.
Before
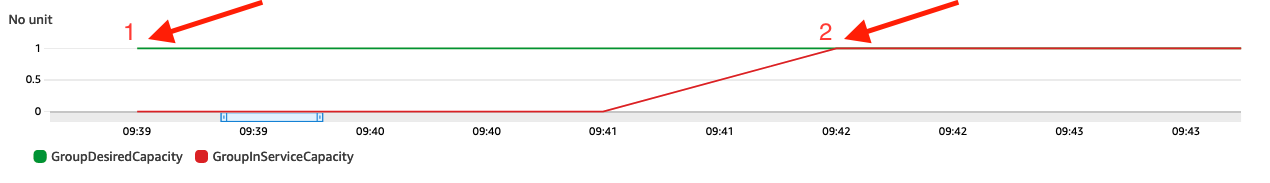 After
After