Install Kube-ops-view
In this step we will install Kube-ops-view from Henning Jacobs. Kube-ops-view will help with understanding our cluster setup in a visual way.
The following lines download the spec required to deploy kube-ops-view using a LoadBalancer Service type and creating a RBAC (Resource Base Access Control) entry for the read-only service account to read nodes and pods information from the cluster.
mkdir $HOME/environment/kube-ops-view
for file in kustomization.yaml rbac.yaml deployment.yaml service.yaml; do mkdir -p $HOME/environment/kube-ops-view/; curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/ec2-spot-workshops/master/content/using_ec2_spot_instances_with_eks/030_k8s_tools/k8_tools.files/kube_ops_view/${file}" > $HOME/environment/kube-ops-view/${file}; done
kubectl apply -k $HOME/environment/kube-ops-view
Open the kube-ops-view site by checking the details about the newly service created.
kubectl get svc kube-ops-view | tail -n 1 | awk '{ print "Kube-ops-view URL = http://"$4 }'
This will display a line similar to Kube-ops-view URL = http://<URL_PREFIX_ELB>.amazonaws.com
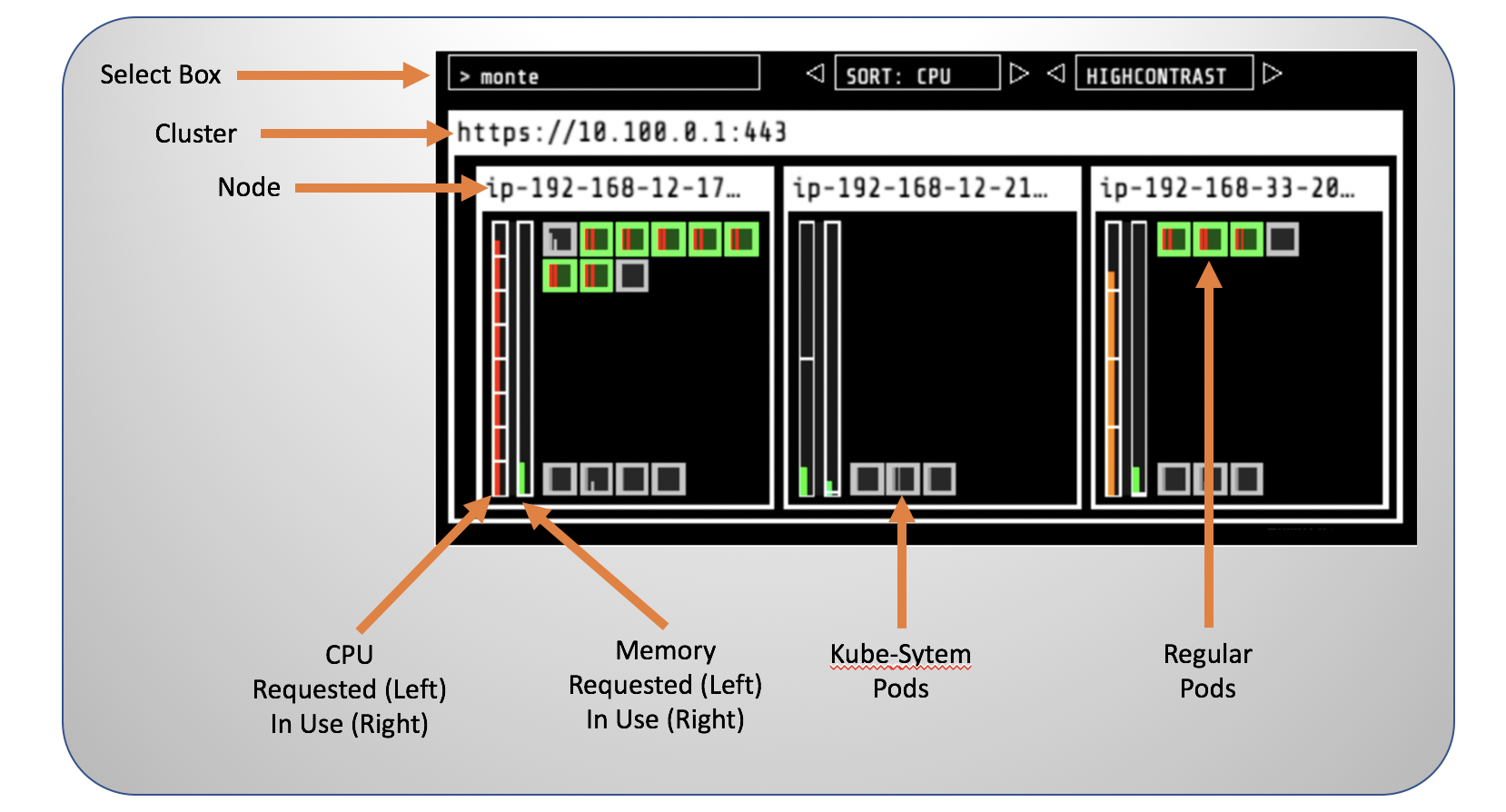
Opening the URL in your browser will provide the current state of our cluster.
You may need to refresh the page and clean your browser cache. The creation and setup of the LoadBalancer may take a few minutes; usually in two minutes you should see kub-ops-view.
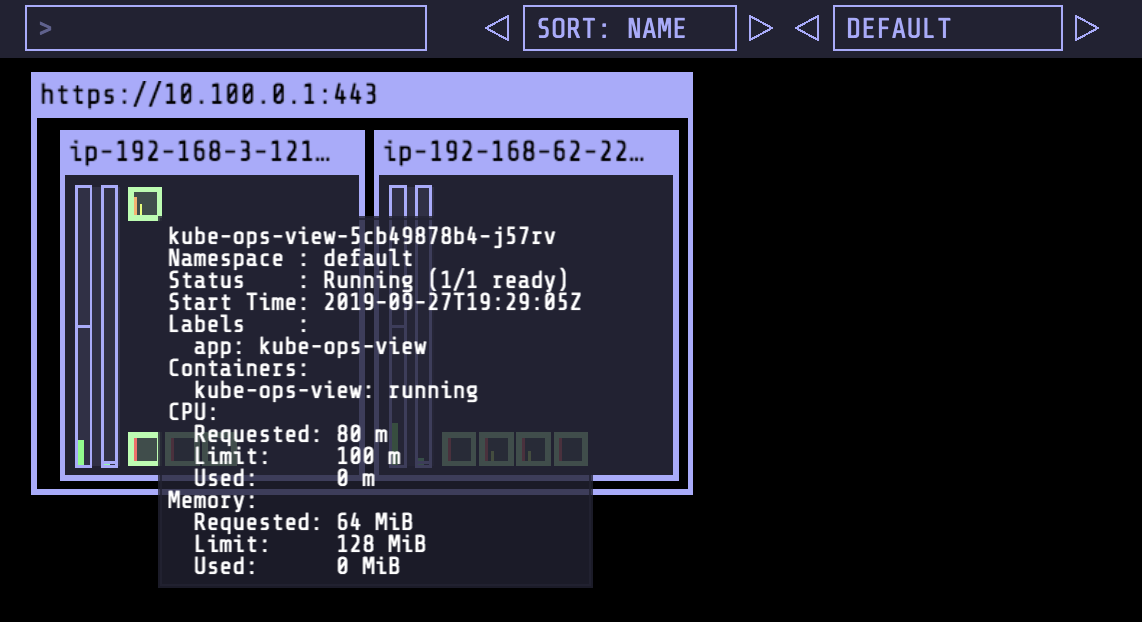
As this workshop moves along and you create Spot workers, and perform scale up and down actions, you can check the effects and changes in the cluster using kube-ops-view. Check out the different components and see how they map to the concepts that we have already covered during this workshop.
Spend some time checking the state and properties of your EKS cluster.