Resilience with Spot Instances
 Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Workshop.
Please note: This workshop version is now deprecated, and an updated version has been moved to AWS Workshop Studio. This workshop remains here for reference to those who have used this workshop before for reference only. Link to updated workshop is here: Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling Workshop.
In this section, you are going to learn about the integrations and approaches to handle EC2 Spot instance interruptions.
Handling Spot Interruptions
When EC2 needs the capacity back in a specific capacity pool (a combination of an instance type in an Availability Zone) it can start interrupting Spot Instances that are running in that AZ, by sending a 2 minute interruption notification, and then terminating the instance. The 2 minute interruption notification is delivered via the EC2 instance meta-data service as well as Amazon EventBridge.
Since November 5th, 2020, EC2 Spot instances also get a notification when they are at elevated risk of interruption via a new signal called EC2 Rebalance Recommendation. This signal can arrive sooner than the two-minute Spot Instance interruption notice, giving you more headroom to react to that upcoming interruption. You can decide to rebalance your workload to new or existing Spot Instances that are not at an elevated risk of interruption.
To help you automating the handling of interruptions, EC2 Auto Scaling has a feature called Capacity Rebalaning that, if enabled, whenever a Spot instance in your Auto Scaling group is at an elevated risk of interruption, it will proactively attempt to launch a replacement Spot Instance. For the feature to work as expected it’s highly recommended that you configure multiple instance types in your Auto Scaling group, and that you use the capacity-optimized allocation strategy. In this case, Auto Scaling will launch the optimal instance type out of your selection of instances based on spare capacity availability at launch time. Once the replacement instance is running and passing health checks, Auto Scaling will then terminate the Spot Instance at an elevated risk of interruption, triggering the configured deregistration delay from the load balancer (if you have a Target Group configured on your Auto Scaling group), and executing termination lifecycle hooks if they are set up (Auto Scaling lifecycle hooks allows you to execute actions before an instance is put in service, and/or before it’s terminated). You can learn more about Capacity Rebalancing here. The diagram below reflects the timeline of a Capacity Rebalancing activity:
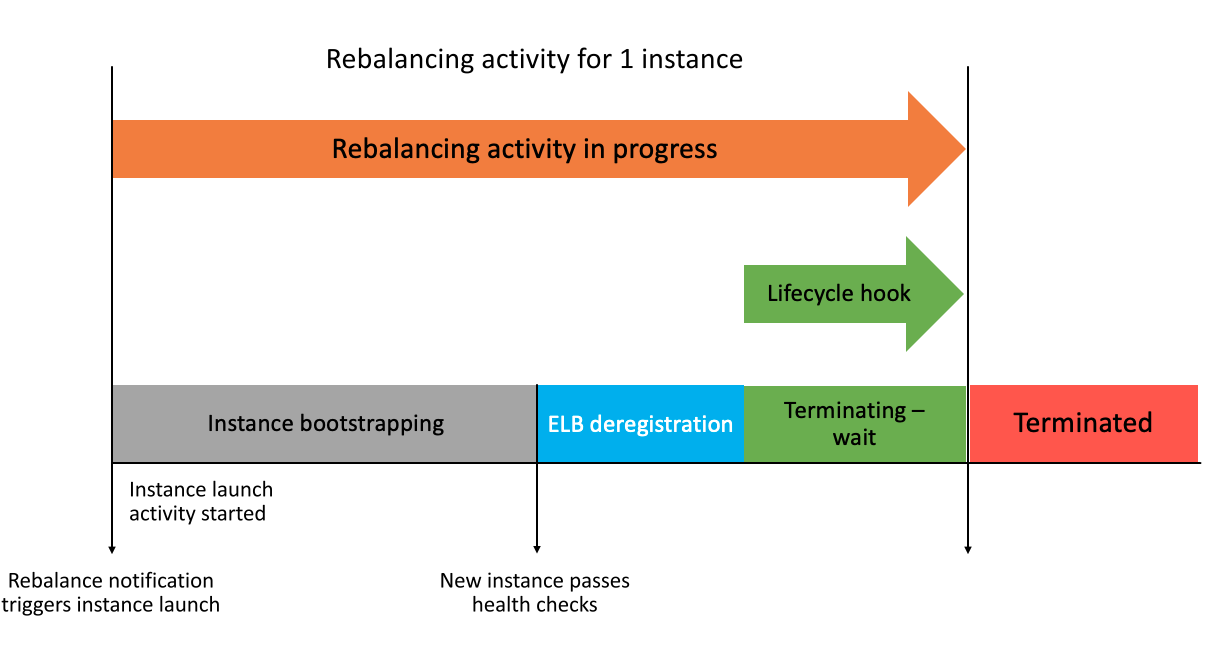
During the Auto Scaling group configuration, we have already enabled Capacity Rebalancing, configured multiple instance types and Availability Zones and the capacity-optimized allocation strategy, so we are all set. If you want to review these configurations again, inspect the asg.json file or go to the Auto Scaling console and check the Purchase options and instance types section of your Auto Scaling group.
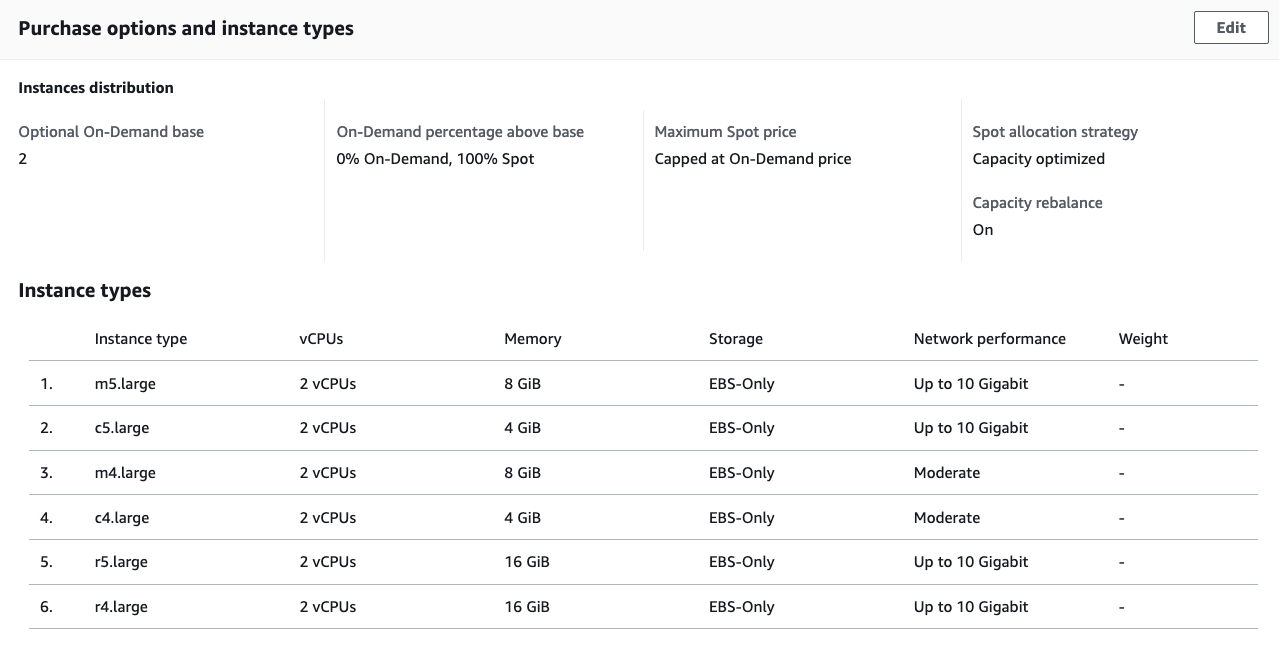
Note that when we have configured the Application Load Balancer, we have configured the deregistration delay of the target group to 90 seconds, so the deregistration of the instance from the ALB completes within the 2 minutes notice. This is because it is not always possible for Amazon EC2 to send the rebalance recommendation signal before the two-minute Spot Instance interruption notice. Therefore, the rebalance recommendation signal can arrive along with the two-minute interruption notice.
Knowledge check
How can you increase the resilience of the web application that you deployed in this workshop, when using EC2 Spot Instances?
- Add an Availability Zone - the EC2 Auto Scaling group is currently deployed in two AZs. By adding an AZ to your application, you will tap into more EC2 Spot capacity pools.
- Add Instance Types - the 6 instance types that are configured in the Auto Scaling group have small performance variability, so it’s possible to run all these instance types in a single ASG and scale on the same dynamic scaling policy. Are there any other instance types that can be added?
Challenges
- By default, a Target Group linked to an Application Load Balancer distributes the requests across its registered instances using a Round Robin load balancing algorithm. Is there anything you could do to spread the load more efficiently if you have backend instances from different instance families that may have slight differences on processing power? Take a look at this article.
If your web application is sensitive to differences in processing power of different instance types you can use the Least Outstanding Requests load balancing algorithm. With this algorithm, as the new request comes in, the load balancer will send it to the target with least number of outstanding requests. Targets processing long-standing requests or having lower processing capabilities are not burdened with more requests and the load is evenly spread across targets. This also helps the new targets to effectively take load off of overloaded targets. You can configure the routing algorithm on the Target Group section within the EC2 console selecting your target group and clicking Actions -> Edit Attributes
Optional exercise: Custom Spot interruption notification handling
In this workshop, you deployed a simple stateless web application and leveraged Capacity Rebalancing for handling the Spot Instance lifecycle. Capacity Rebalancing works great for this use case, as it will automatically take care of bringing up replacement capacity when Spot instances are at an elevated risk of interruption and gracefully attempt to finish in-flight requests coming from the Application Load Balancer.
For other EC2 Auto Scaling workloads, like queue workers or other similar batch processes, you may prefer to execute actions when the EC2 Rebalance Recommendation signal is issued (like stop consuming new jobs) but to not terminate the instance until in-flight job processing has finished and/or act only when the two-minute instance termination warning arrives. For these cases, you can build your own handling logic by leveraging Amazon EventBridge notifications, AWS Lambda and / or a local script that consumes the EC2 metadata service notifications. As an example, you can find here a sample solution.
In this optional exercise, you will deploy an Amazon EventBridge rule to catch the EC2 Spot Instance Interruption warning events and an AWS Lambda function to automatically detach the soon-to-be-terminated instance from the EC2 Auto Scaling group.
By calling the DetachInstances API you achieve two things:
-
You can specify on the API call whether to keep the current desired capacity on the Auto Scaling group, or decrement it by the number of instances being detached. By keeping the same desired capacity, Auto Scaling will immediately launch a replacement instance.
-
If the Auto Scaling group has a Load Balancer or a Target Group attached (as we have in this workshop), the instance is deregistered from it. Also, if connection draining is enabled for your Load Balancer (or Target Group), the Auto Scaling group waits for in-flight requests to complete (up to the configured timeout, which we have set up to 90 sec).
You can learn more about the Detaching EC2 Instances from an Auto Scaling group here.
All this isn’t needed if you use Capacity Rebalancing, as the service handles this for you when receiving an EC2 Rebalance Recommendation. However if you need to build a custom workflow to respond to Spot interruptions, you can use this example as a starting point. The exercise will also guide you to mock a Spot Instance interruption, so you can experience how the different components behave (which is similar to the built-in Capacity Rebalancing functionality behavior).
We provide you with a sample EC2 Spot Interruption handler here that you can easily deploy via the Serverless Application Repository.
-
Go to the
Available applicationssection of the Serverless Application Repository console -
Under
Public applicationssection, mark the checkbox Show apps that create custom IAM roles or resource policies and typeec2-spot-interruption-handler, then click on the application. You can also access the application directly clicking this link -
Scroll to the bottom and on the
Application settingssection, leave the default settings and mark the checkbox I acknowledge that this app creates custom IAM roles and resource policies. Then clickDeploy. -
Allow a couple of minutes for the application to be deployed. Take this time to browse the solution details on GitHub.
The serverless application has configured the following resources:
- An AWS Lambda function that receives Spot Interruption notifications, checks if the instance is part of an Auto Scaling group (and if it’s been tagged with Key:
SpotInterruptionHandler/enabledValue:true) and to then call the DetachInstances API of EC2 Auto Scaling to start connection draining and launch a replacement instance. Feel free to go to the AWS Lambda console and inspect theSpotInterruptionHandlerfunction. - An Amazon EventBridge event rule to capture Spot Instance interruption notifications and trigger the above Lambda function. Feel free to go to the Amazon EventBridge console to inspect the rule.
- An IAM role for the Lambda function to be able to call the AWS API.
If you check the Auto Scaling group instances, you will see they’ve been already tagged appropriately for SpotInterruptionHandler to take actions if one of its Spot Instance is interrupted (check the asg.json file and you’ll see the tag there). At this stage, our infrastructure is ready to respond to Spot Interruptions.
We can’t simulate an actual EC2 Spot Interruption, but we can invoke the Lambda Function with a simulated EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning event for one of or Auto Scaling group instances, and see the result.
- Go to the AWS Lambda console and open the SpotInterruptionHandler function. In the top right corner, click the dropdown menu Select a test event -> Configure test events
- With Create a new test event selected, provide an Event name (i.e TestSpotInterruption). In the event text box, paste the following:
{
"version": "0",
"id": "92453ca5-5b23-219e-8003-ab7283ca016b",
"detail-type": "EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning",
"source": "aws.ec2",
"account": "123456789012",
"time": "2019-11-05T11:03:11Z",
"region": "eu-west-1",
"resources": [
"arn:aws:ec2:eu-west-1b:instance/<instance-id>"
],
"detail": {
"instance-id": "<instance-id>",
"instance-action": "terminate"
}
}
- Replace both occurrences of "<instance-id>" with the instance-id of one of the Spot Instances that are currently running in your EC2 Auto Scaling group (you can get an instance-id from the
Instance managementtab in the bottom pane of the EC2 Auto Scaling groups console ). You don’t need to change any of the other parameters in the event json. - Click Create
- With your new test name (i.e TestSpotInterruption) selected in the dropdown menu, click the Test button.
- The execution result should be succeeded and you can expand the details to see the successful log message: “Interruption response actions completed for instance i-0156bedcef61187e8 belonging to runningAmazonEC2WorkloadsAtScale”
- Go back to the EC2 Auto Scaling groups console, click on the myEC2Workshop Auto Scaling group and under the Activity tab in the bottom pane, you should see a Detaching EC2 instance activity, followed shortly after by a Launching a new EC2 instance activity. Notice the status
WaitingForELBConnectionDrainingon the detached instance. You will find the deregistration timeout configured on themodify-target-group.jsonfile. - Go to the EC2 ELB Target Groups console and click on the myEC2Workshop Target Group, go to the Targets tab in the bottom pane, you should see the instance in
drainingstatus.
Great result! by leveraging the EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning, the Lambda Function detached the instance from the Auto Scaling group and the ELB Target Group, thus draining existing connections, and launching a replacement instance before the current instance is terminated.
Optionally, you can also configure the solution to execute commands on the instances when receiving a Spot Interruption Notice leveraging AWS Systems Manager. You can find more information on GitHub