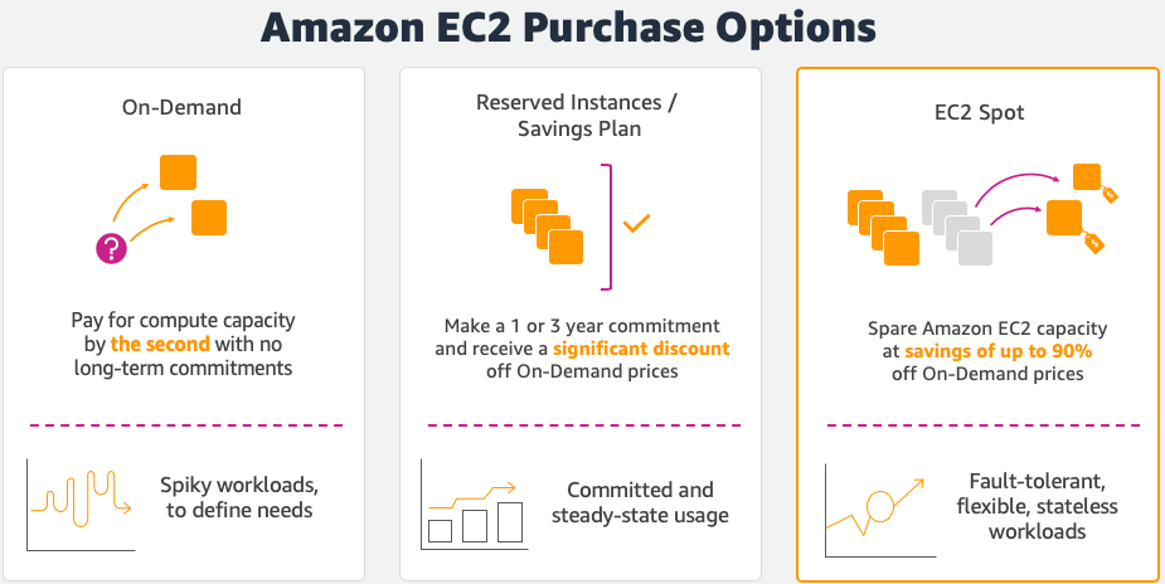
In this workshop, you will learn how to provision, manage, and maintain your Kubernetes clusters with Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS ) scaling optimally using Karpenter . Karpenter is a node lifecycle management solution used to scale your Kubernetes cluster. Karpenter observes incoming pods and launches the right-sized Amazon EC2 Instance appropriately for the workload. Instance selection decisions are intent based and driven by the specification of incoming pods, including resource requests and scheduling constraints.